Conductivity Probe K 1.0 - Atlas Scientific
Conductivity Probe K 1.0 - Atlas Scientific
An E.C. (electrical conductivity) probe measures the electrical conductivity of a solution. It is commonly used in hydroponics, aquaculture and freshwater systems to monitor the number of nutrients, salts or impurities in the water. Inside the conductivity probe, two electrodes are positioned opposite from each other, an AC voltage is applied to the electrodes causing cations to move to the negatively charged electrode, while the anions move to the positive electrode. The more free electrolyte the liquid contains, the higher the electrical conductivity.
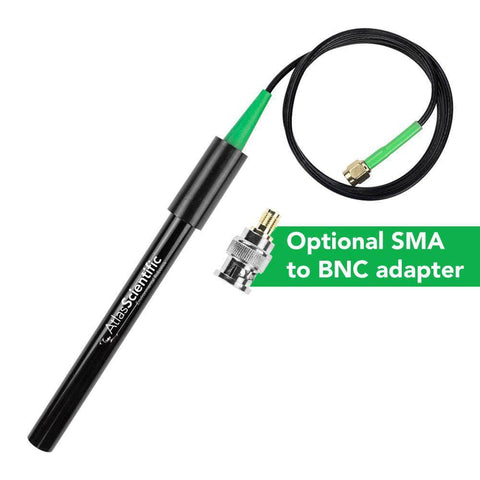
A conductivity probe is a very simple device. It is just two conductors with a fixed surface area at a fixed distance from each other. This distance and surface area is known as the conductivity cell. The cells distance and surface area is quantified as the conductivity cells K constant.
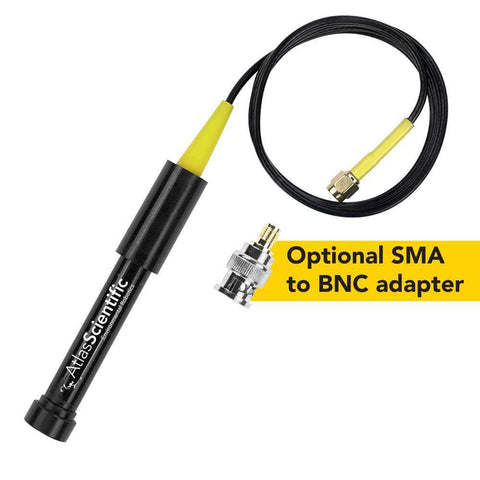
This Conductivity Probe can be fully submerged in fresh water or salt water, up to the SMA connector indefinitely.
| Reads | Conductivity |
| Range | 5 − 200,000 μS/cm |
| Accuracy | +/ – 2% |
| Response time | 90% in 1s |
| Temperature range °C | 1 − 110 °C |
| Max pressure | 3,447 kPa (500PSI) |
| Max depth | 352m (1,157 ft) |
| Connector | Male SMA / Male BNC (optional) |
| Cable length | 1 meter |
| Internal temperature sensor | No |
| Time before recalibration | ~10 years |
| Life expectancy | ~10 years |